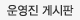|
탄성계수를 찾아보다가 마침, 스노보드 데크 소재 및 나무 샌드위치 접합을 그대로 소개하는 글을 보게 되서 첨부하며 간략하게 소개합니다. *번역은 구글번역을 이용하시면 수월하실 겁니다.
[간략정리]
탄성과 하드함은, 물리적으로는 모두 '탄성계수'로 논하게 됩니다.
*물론 영계수 및 항복강도라는 파괴와 관련된 부분은 별도로 논의됩니다. 보통 거의 같이 가긴 합니다만 또 다릅니다.
다시 말해서, 덜 하드하면 부드럽다는 뜻이고 즉슨 상대적으로 진동을 잘 잡아줍니다. 대신 탄성은 떨어집니다.
*그러나 유리같이 경도가 너무 쎈 것은..그냥 깨져버리죠.
대충 카본섬유는 P-Tex(E or S Fiber Glass) 및 알루미늄인 티타날(2024-T3 Aluminum?) 에 비해 2.5배~3배정도의 탄성계수를 가지는 것으로 나옵니다. 즉슨 항복강도에 이르기 전까지는, 2.5배 ~3배까지 더 단단하고 더 빠른 탄성회복력을 가집니다.
*물론 항복강도도 사실 더 높아서 그냥 더 단단합니다.
그리고 철(4130 Steel)과는 거의 같습니다.
*사실 카본섬유가 10%쯤 살짝 좀 더 높네요. 철은 종류가 많으니까 이 정도는 무시합니다. 참, 스테인레스는 일반적으로 철이라 불리는 탄소강보다 무릅니다.
[결론]
- 탄성계수로 볼때, 피텍스나 티타날이나 진동흡수 정도는 거의 동일하다. 만약 큰 차이가 난다면, 적용 두께/무게 차이일 확률이 클 것이다. *그러나 섬유에 따라 압축/인장 탄성계수는 가해지는 방향에 따라 또 다르기에 데크토션을 고려하면 완벽하진 않습니다. 티타날은 금속성이니 만큼 아마 거의 일률적일 확률이 높긴 합니다. 나쁘게 말하면 방향에 따라 특성없이 동일한 것이죠.
- 이종 재질을 접합하는 것은 상당히 까다로운 작업이며 재질별로 특수한 수지가 쓰이는 경우가 많은데, 아마 금속성인 티타날용 접합수지가 가장 비쌀 것이다. *카본섬유와 유리섬유용 접합수지는 거의 비슷한 수준일 것으로 추정합니다. 원래 두 섬유는 아주 오래전부터 추가되어 접착되어 왔던 섬유이기도 합니다. 티타날은 비교적 신생이죠.
- 진동흡수를 원한다면 피텍스 또는 티타날을 쓰나 (보통 상판에 적용하는 것 같습니다. 피텍스는 데크에 따라 내부에 이미 들어간 경우도 꽤 있습니다.) 그만큼 탄성이 감소하는 것은 감안해야한다. *즉 리바운딩이나 아찔한 맛은, 들어간 만큼 덜할 것입니다. 대신 그만큼 안정적일 것입니다.
[출처페이지]
What Is Carbon Fiber? | Understanding Carbon Composites (dragonplate.com)
[일부출처]
Strength, Stiffness, and Comparisons With Other Materials
Carbon fiber is extremely strong. It is typical in engineering to measure the benefit of a material in terms of strength to weight ratio and stiffness to weight ratio, particularly in structural design, where added weight may translate into increased lifecycle costs or unsatisfactory performance. The stiffness of a material is measured by its modulus of elasticity. The modulus of carbon fiber is typically 33 msi (228 GPa) and its ultimate tensile strength is typically 500 ksi (3.5 Gpa). High stiffness and strength carbon fiber materials are also available through specialized heat treatment processes with much higher values. Compare this with 2024-T3 Aluminum, which has a modulus of only 10 msi and ultimate tensile strength of 65 ksi, and 4130 Steel, which has a modulus of 30 msi and ultimate tensile strength of 125 ksi.
(중략)
What is a Composite Sandwich Structure?
A composite sandwich combines the superior strength and stiffness properties of carbon-fiber with a lower density core material. In the case of Dragonplate sandwich sheets, the carbon-fiber creates a thin laminate skin over a foam, honeycomb, balsa, or birch plywood core. By strategically combining these materials, one is able to create a final product with a much higher stiffness-to-weight ratio than with either alone. For applications where weight is critical, carbon-fiber sandwich sheets may be the right fit.
A composite sandwich structure is mechanically equivalent to a homogeneous I-Beam construction in bending.
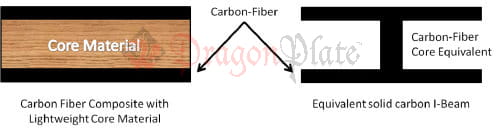 Figure 1: Diagram showing carbon-fiber composite sandwich and equivalent I-Beam
Figure 1: Diagram showing carbon-fiber composite sandwich and equivalent I-Beam
Referring to the picture of the sandwich structure, at the center of the beam (assuming symmetry) lies the neutral axis, which is where the internal axial stress equals zero. Moving from bottom to top in the diagram, the internal stresses switch from compressive to tensile. Bending stiffness is proportional to the cross-sectional moment of inertia, as well as the material modulus of elasticity. Thus for maximum bending stiffness, one should place an extremely stiff material as far from the neutral axis as possible. By placing carbon fiber furthest from the neutral axis, and filling the remaining volume with a lower density material, the result is a composite sandwich material with high stiffness to weight ratio.
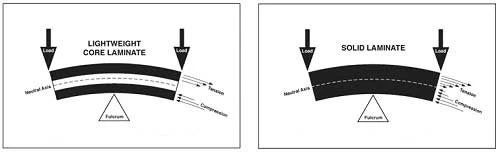 Figure 2: Comparison of internal stress distribution for solid laminate and sandwich construction in bending.
Figure 2: Comparison of internal stress distribution for solid laminate and sandwich construction in bending.
(생략)